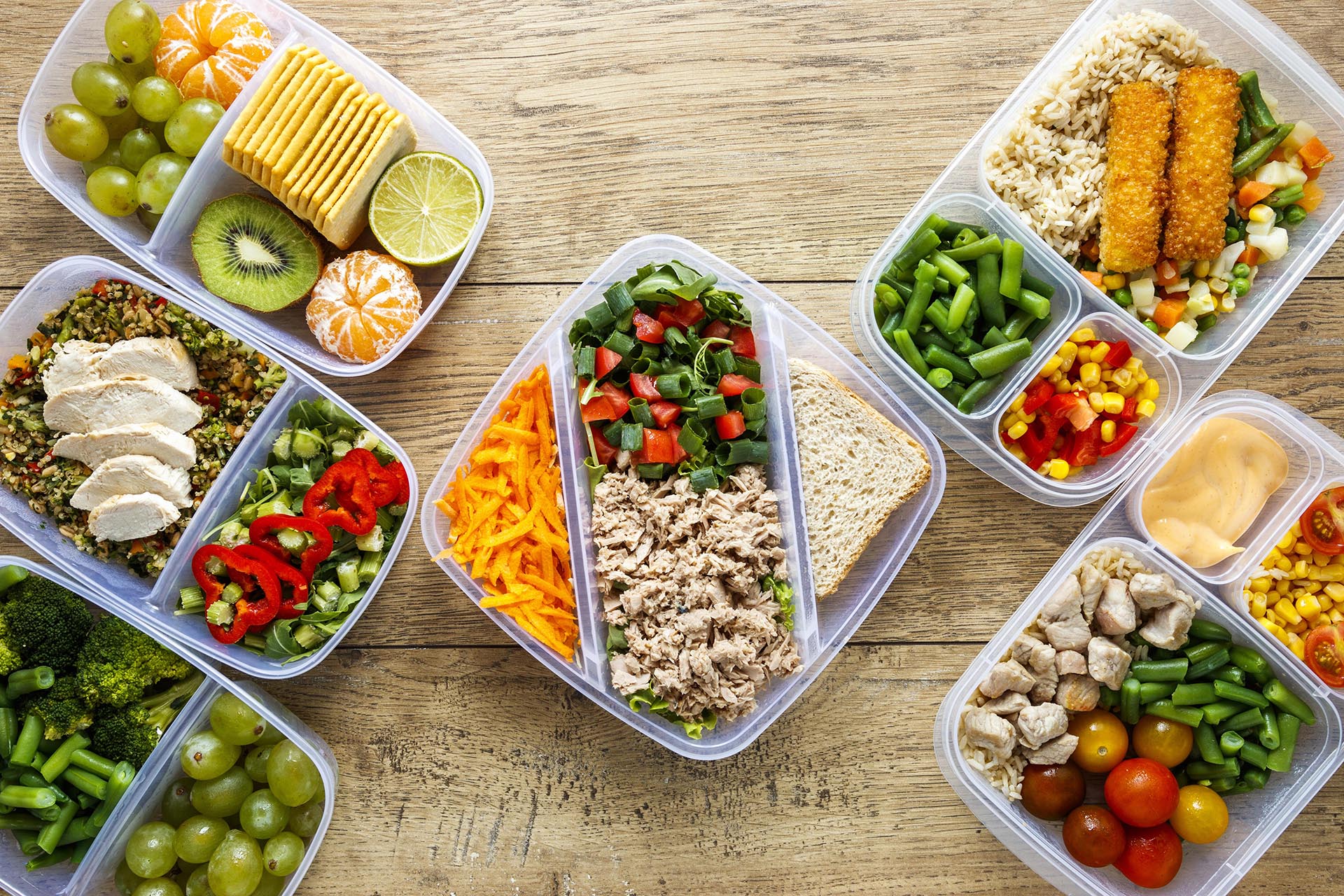
Web Menu
Product Search
Exit Menu
Comprehensive analysis of PP plastic food tray: material characteristics, advantages and application scenarios
1. What is a PP plastic food tray?
The Origin and Popularity of PP Material
Polypropylene was first developed in the mid-20th century and quickly became popular due to its superior performance compared to other plastics. Unlike polystyrene (PS) or polyethylene terephthalate (PET), PP is more flexible, more resistant to chemical interactions, and can withstand higher temperatures. These qualities make it ideal for applications that involve both hot and cold food storage.
In recent years, as the food delivery industry and ready-to-eat meal sector have expanded globally, the demand for safe, lightweight, and microwave-safe packaging has skyrocketed. PP food trays have become the go-to choice for many restaurants, food suppliers, supermarkets, and catering services because they meet both functional requirements and regulatory safety standards.
Material Characteristics of PP Plastic
Chemical Composition: PP is a polymer made from propylene monomers. Its molecular structure gives it an excellent balance of strength, elasticity, and thermal stability. Unlike some plastics, it does not release harmful substances when exposed to heat, which is essential for food-contact safety.
Food-Safe Nature: Polypropylene is widely recognized as food-grade and is compliant with global standards such as FDA, EU food safety regulations, and LFGB. This ensures that PP trays do not leach toxic chemicals into food, even when subjected to high temperatures.
High Temperature Resistance: One of PP’s standout features is its ability to withstand temperatures up to 120°C, making it suitable for microwave heating and hot food storage. At the same time, it remains stable at low temperatures, making it an excellent choice for freezing or refrigerating foods.
Corrosion and Chemical Resistance: PP is inert to acids, bases, and oils, which means it does not degrade or react when in contact with different types of foods—whether they are acidic, oily, or heavily spiced.
Lightweight yet Durable: With a low density (approximately 0.9 g/cm³), PP trays are lightweight, which reduces transport costs and enhances convenience. Despite being light, they maintain good structural strength, preventing cracking or warping under normal usage.
How Are PP Plastic Food Trays Made?
The manufacturing of PP plastic food trays generally involves two main processes: injection molding and thermoforming (or blistering).
Injection Molding: In this process, melted PP resin is injected into a mold, where it cools and solidifies to form the shape of the tray. Injection molding allows for precise customization, such as creating trays with multiple compartments, reinforced edges, or unique designs.
Thermoforming/Blistering: This technique involves heating a thin PP sheet until it becomes pliable, then forming it into a mold using vacuum pressure. This process is often used for lightweight, disposable trays, commonly seen in supermarkets for packaging fruits, vegetables, or ready meals.
Both methods ensure that the trays are uniform, smooth, and suitable for automated packaging machines, which is crucial for mass production in the food industry.
Why is PP the Preferred Material for Food Trays?
The popularity of PP in food packaging stems from its balance of functionality, safety, and cost-effectiveness. For example:
Microwave and Freezer Compatibility: Consumers and food businesses appreciate that a PP tray can go from freezer to microwave without risk of breaking or releasing harmful substances.
Transparency and Aesthetics: PP can be manufactured in a clear or opaque form, allowing brands to showcase the freshness of food while maintaining durability.
Odor and Taste Neutrality: Unlike some lower-grade plastics, PP does not retain or impart smells or tastes, ensuring that the original flavor of food is preserved.
Eco-Friendly Advantage: While PP is not biodegradable, it is 100% recyclable. In many regions, recycling facilities process PP into reusable materials, which helps reduce environmental impact compared to non-recyclable plastics.
2. Main material characteristics of PP plastic food tray
High Food Safety and Regulatory Compliance
The foremost advantage of PP plastic food trays lies in their outstanding food safety performance. Polypropylene is widely recognized as a food-contact-safe plastic, meaning it is free from harmful chemicals and does not interact with the food it holds. Unlike some plastics that may leach toxic substances under heat, PP is inherently stable, ensuring that no unwanted chemicals are released, even when used in microwaves or with hot foods.
One of the most significant aspects of PP is that it is free from Bisphenol A (BPA), a controversial chemical often found in other plastics such as polycarbonate. BPA has been linked to various health concerns, including endocrine disruption, which makes BPA-free materials like PP the preferred choice for food packaging, especially in sensitive applications such as baby food containers or ready-to-eat meals.
PP trays comply with stringent international safety standards, including FDA (U.S. Food and Drug Administration) and LFGB (German Food, Consumer Goods and Feed Code). These certifications assure consumers and businesses that the material has been tested for toxicity, heavy metals, and potential contaminants, guaranteeing that PP trays are safe for direct food contact.
Excellent High and Low Temperature Resistance
A notable characteristic of PP plastic food trays is their wide temperature tolerance. They can withstand temperatures ranging from approximately -20°C to 120°C, which allows them to perform reliably in both freezing and heating applications. This makes them ideal for freezer-to-microwave usage—a feature highly valued by consumers who seek convenience.
Unlike certain plastics that become brittle in cold conditions, PP maintains its structural integrity and does not crack or warp in sub-zero environments. This property is particularly important for packaging frozen goods such as meat, seafood, or ready-to-cook meals. Similarly, PP trays can handle hot foods and even microwave reheating without releasing toxic fumes or deforming.
This dual resistance to cold and heat means PP trays can be used in diverse scenarios:
Cold storage: Perfect for chilled salads, desserts, and frozen entrees.
Hot food delivery: Suitable for soups, curries, and freshly cooked dishes.
Microwave heating: Designed for modern lifestyles where reheating convenience is a must.
Strong Chemical and Corrosion Resistance
Food packaging often involves contact with a wide range of substances—oily, acidic, or alkaline foods, as well as sauces and seasonings. PP’s chemical stability ensures that these trays remain unaffected by such substances. It is highly resistant to acids, bases, and many chemical solvents, which means the tray will not degrade or break down when exposed to food with strong flavors, such as vinegar-based dressings, tomato sauces, or spicy marinades.
PP does not absorb oils or flavors, ensuring that the tray does not alter the taste, aroma, or appearance of the food. This property makes it particularly advantageous for multi-compartment trays where different types of food are stored together, as it prevents cross-contamination of flavors.
From an industrial perspective, this chemical resistance also ensures that PP trays can be safely washed and reused (in the case of thicker, non-disposable designs) without losing quality, even when exposed to detergents or disinfectants.
Lightweight yet Mechanically Strong
Another defining characteristic of PP plastic food trays is their lightweight structure, attributed to the low density of polypropylene—about 0.9 g/cm³, which is lower than many other commonly used plastics like PET or PVC. Despite being light, PP has excellent mechanical strength and toughness. It offers a balanced combination of flexibility and rigidity, ensuring that the tray is impact-resistant and less prone to breaking or cracking during transportation, stacking, or everyday handling.
For businesses, the lightweight nature of PP translates into reduced transportation costs and improved handling efficiency, particularly when dealing with bulk packaging for supermarkets, catering, or takeaway services. At the same time, its toughness ensures that even thin-walled PP trays provide reliable protection for the food they hold, minimizing the risk of leaks or damage.
Recyclability and Environmental Responsibility
In today’s environmentally conscious world, recyclability has become a key factor in packaging material selection. PP plastic food trays are 100% recyclable, meaning they can be collected, processed, and reused to create new products such as household items, automotive components, or even new food packaging. This recyclability aligns with global sustainability goals and helps businesses reduce their carbon footprint.
PP’s durability allows for multiple reuse cycles in cases where thicker trays are designed for repeat use, such as in catering services, cafeteria settings, or meal delivery systems. Compared to single-use plastics like expanded polystyrene (EPS), PP trays present a more eco-friendly alternative.
In addition to being recyclable, PP is also considered to have a lower environmental impact during production compared to some other plastics. It requires relatively less energy to manufacture, and its lightweight nature reduces emissions during transportation. Many manufacturers are also exploring bio-based polypropylene (derived from renewable resources) to further reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
Versatility in Design and Applications
Beyond the five key characteristics mentioned above, another noteworthy advantage of PP material is its design flexibility. PP can be molded into a wide variety of shapes, sizes, and colors to meet diverse market demands. Whether it’s a compartmentalized tray for airline meals, a shallow tray for sushi and desserts, or a deep container for soups and sauces, PP’s properties allow for customization without sacrificing strength or safety.
This design versatility also makes PP compatible with automated sealing and packaging machines, an essential requirement in modern food production lines. Its smooth surface and consistent structure make it easy to heat-seal with films, ensuring airtight packaging and extended shelf life for perishable products.
3. Advantages of PP plastic food tray
Moderate Price and High Cost-Performance
One of the most significant advantages of PP plastic food trays is their cost-effectiveness. The raw material for PP is widely available and relatively inexpensive compared to other food-grade plastics such as PET (polyethylene terephthalate) or PLA (polylactic acid). This affordability is further enhanced by the high production efficiency of PP—it is easy to mold, requires less energy to manufacture, and can be produced in large volumes at low cost.
For businesses, this translates to lower packaging expenses without compromising on quality or safety. Whether it’s a small restaurant or a large-scale food manufacturer, PP trays offer an optimal balance between price and functionality. PP trays are durable and reusable (for thicker versions), meaning they can be used multiple times, effectively reducing the cost per use.
Compared to alternatives like aluminum containers or glass dishes, PP trays offer lower transportation and storage costs because of their lighter weight and stackable design. This cost-saving factor is particularly important for industries where margins are tight, such as fast-food chains and meal delivery services.
Compatibility with Automated Packaging Equipment
In modern food production and catering industries, automation is key to efficiency and consistency. PP plastic food trays are designed to be fully compatible with a variety of film-sealing machines and automated packaging lines. Their smooth surface and consistent shape allow for precise sealing with plastic films or lids, ensuring that food is packaged securely and hygienically.
The ability to integrate seamlessly with heat-sealing or vacuum-sealing systems is critical for businesses that require high-volume, standardized food packaging—such as supermarket ready meals, airline catering, and large-scale meal prep operations. PP trays’ dimensional stability ensures that they remain flat and uniform under heat-sealing conditions, which reduces sealing errors and product waste.
Another major advantage is that PP trays can be customized with anti-fog or high-clarity sealing films, ensuring that food remains visible and appealing on store shelves. This compatibility with advanced packaging technologies directly contributes to extended shelf life, reduced food spoilage, and enhanced presentation.
Anti-Leakage Design for Liquid and Semi-Liquid Foods
One of the standout features of PP plastic food trays is their ability to effectively prevent leaks, making them ideal for foods containing soups, sauces, gravies, or dressings. Many PP trays are manufactured with reinforced edges and tight-fitting lids, which work together with heat-sealing films to create an airtight, leak-proof seal.
This anti-leakage feature is particularly valuable for takeout and delivery services, where food must be transported over long distances without spilling. Restaurants and catering services benefit from fewer customer complaints and improved brand reputation when they use packaging that ensures food arrives in perfect condition.
The structural design of PP trays also contributes to their leak resistance. Many trays include raised compartments or dividers that prevent liquids from mixing between food items. This is especially useful for multi-course meals, bento boxes, or meal prep containers where separation of ingredients is essential.
Customization to Enhance Brand Image
Brand identity and customer experience are closely tied to packaging aesthetics. PP plastic food trays offer exceptional flexibility in terms of color, shape, size, and design, which allows businesses to create packaging that reflects their unique brand image.
For instance:
Color customization: PP trays can be manufactured in a range of colors—from classic black and white to transparent or vibrant shades—to match a brand’s visual identity.
Shape and size customization: Whether it’s a single-compartment tray for pasta dishes or a multi-compartment tray for full meals, PP trays can be designed to suit different menu items and portion sizes.
Logo embossing or printing: Many manufacturers offer custom molds with brand logos or patterns, enhancing the premium feel of the packaging and increasing brand visibility.
This customization not only improves the visual appeal of the product but also enhances the consumer experience, as attractive, well-designed packaging often translates into perceived higher quality of the food itself. For retail environments such as supermarkets, eye-catching tray designs can significantly boost product sales.
Long Service Life and Reusability
While many PP food trays are designed for single-use convenience, thicker and more robust PP trays are suitable for repeated use, especially in commercial or institutional settings like cafeterias, hospitals, and catering services. These reusable trays can be washed (even in dishwashers, depending on the design) and reused multiple times without degrading in quality.
The durability of PP ensures that the trays retain their shape and structural integrity even after prolonged use. This feature not only reduces waste but also makes them a cost-effective option for bulk food services. Compared with fragile materials like paperboard or foam, PP trays are more resistant to cracking, bending, or soaking through when in contact with liquids.
For meal-prep businesses, the reusability of PP trays offers additional convenience. Customers can store leftovers, reheat meals in the microwave, or freeze portions without needing additional containers. This multi-functional usability provides added value, making PP trays an attractive choice for both businesses and consumers.
Additional Advantages in Practical Use
Beyond the five primary benefits outlined above, PP plastic food trays also offer several secondary advantages that enhance their practicality:
Stackability: PP trays are designed for efficient stacking, reducing storage space in kitchens or warehouses.
Lightweight Transport: Their low weight minimizes shipping costs, particularly for businesses handling large volumes.
Hygiene and Safety: PP trays can be easily sealed, keeping food fresh and protected from contamination during handling and delivery.
Versatile Applications: Suitable for a wide range of food types—from fresh salads to hot, saucy dishes—PP trays cater to diverse culinary needs.
4. Application scenarios of PP plastic food trays
Takeout and Fast Food
In fast-paced modern life, takeout and fast food have become the first choice for many consumers, and PP plastic food trays are one of the most representative packaging products in this field.
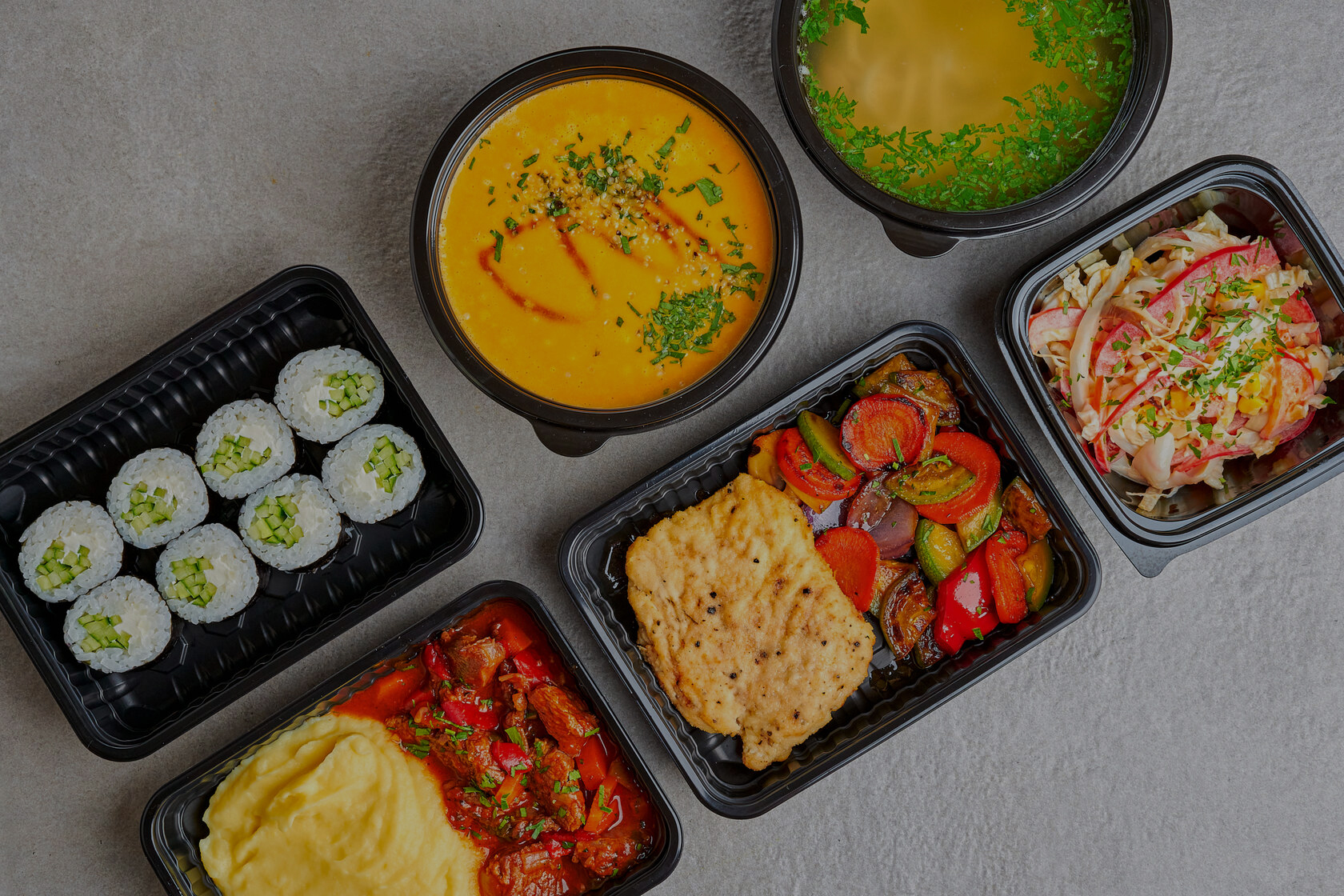
Common forms: including bento boxes, partitioned dining trays, heat-sealable transparent boxes, cover bowls, etc. These trays usually have a partition structure that allows you to place staples, side dishes and soups in the same container to avoid mixing different ingredients and affecting the taste.
Advantages:
Convenient to carry and eat: PP trays are usually equipped with sealing covers or film seals for easy packaging and take-out. Consumers can eat them directly in the tray without additional transfer of tableware.
Maintain food quality: Many takeaway foods are hot dishes, and PP trays have excellent high temperature resistance and can be directly used for microwave heating, allowing customers to quickly heat food at home or in the office.
Branded packaging: Fast food chains and takeaway platforms often display brand logos and special colors by customizing PP trays, improving the professionalism and classiness of takeaway products.
With the continuous development of the takeaway industry, the demand for PP pallets in this field is still rising. Its lightweight and leak-proof design is especially suitable for soups, bibimbap, pasta, curry and other "juicy" meals.
Supermarket Fresh Food and Cooked Food Area
PP plastic food trays are widely used in refrigerated or room temperature areas in various supermarkets, and are often used to package fresh meat, cooked food, vegetables and ready-to-eat products.
Packaged meat and seafood: The anti-leakage design of the PP tray can prevent blood or juice from leaking, keeping the shelves clean and hygienic. Many supermarkets use a combination packaging method of tray + plastic wrap, which can not only show the fresh appearance of the ingredients, but also prevent secondary pollution.
Delicious food packaging: PP trays are commonly used in the cooked food area to hold braised food, fried chicken, sushi, salad and other foods. This type of pallet can directly heat seal the film to ensure that the food is not affected by the external environment during transportation and sale.
Advantages and trends:
Good transparency: Some PP trays adopt a high transparency design, allowing customers to see the freshness of food at a glance.
Suitable for automatic packaging: Large chain supermarkets usually use automated film sealing machines, and the standardized size of PP pallets can quickly match the equipment and improve packaging efficiency.
Easy to store and stack: PP pallets have a standardized appearance and are not easy to deform when stacked, which is conducive to warehousing and display.
With the development of fresh food e-commerce, more and more ready-to-eat bentoes, salad bowls, etc. also use PP trays as packaging materials to meet the demand for "buy now and eat".
Cold Chains and Frozen Foods
Cold chain transportation and quick-frozen food have high requirements for the low-temperature resistance of packaging containers, and PP plastic pallets have particularly outstanding performance in this regard.
Application scenarios:
Semi-finished foods such as quick-frozen dumplings and dumplings: These foods need to be frozen and stored for a long time in an environment of -18°C or even lower, while PP trays can maintain toughness under low temperature conditions and will not crack easily like some brittle plastics.
Refrigerated salads, fresh fruit platters: The lightweight and sealable properties of PP trays are ideal for cold chain distribution, keeping the food fresh during transportation.
Advantages:
Low temperature stability: PP trays can remain strong at low temperatures and will not deform or crack due to temperature differences.
Direct heating: After consumers take out semi-finished food from the freezer, they can directly put it in a microwave or hot water to heat it, saving the trouble of replacing the container.
Sanitary and safety: In cold chain logistics, PP pallets can effectively block external pollution and ensure that food maintains high quality throughout transportation.
Baking and Desserts
Baked goods and dessert packaging not only needs to be beautiful, but also prevents food from deforming or getting damp. PP trays also perform well in packaging of these products.
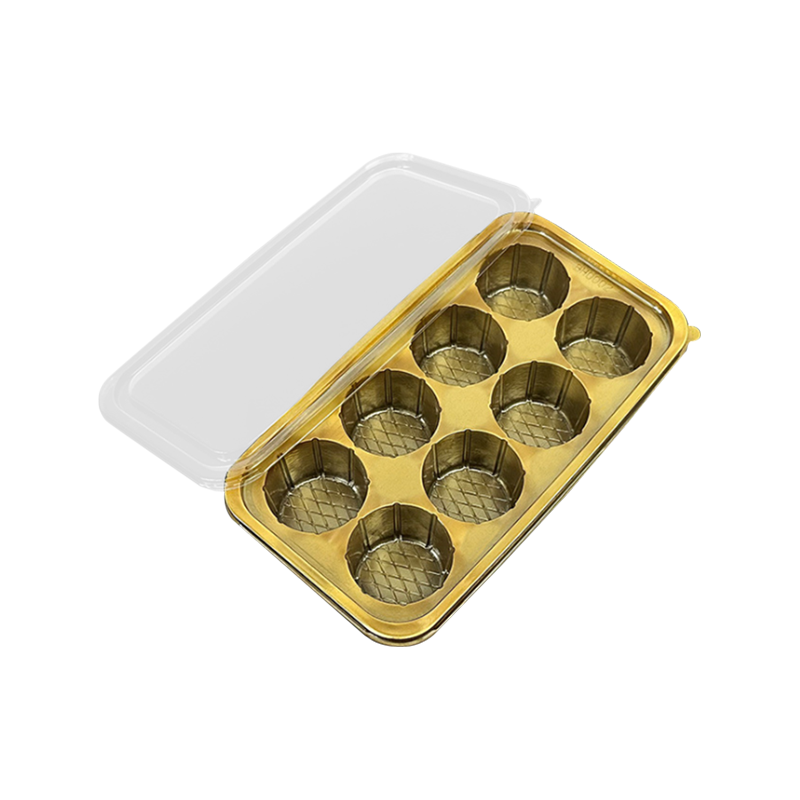
Application examples: cake base, cookie tray, mousse cake cup, dessert platter, etc.
Advantages:
Strong structural support: PP trays can withstand the weight of soft foods such as cakes and cream to avoid affecting the shape of the finished product due to soft packaging.
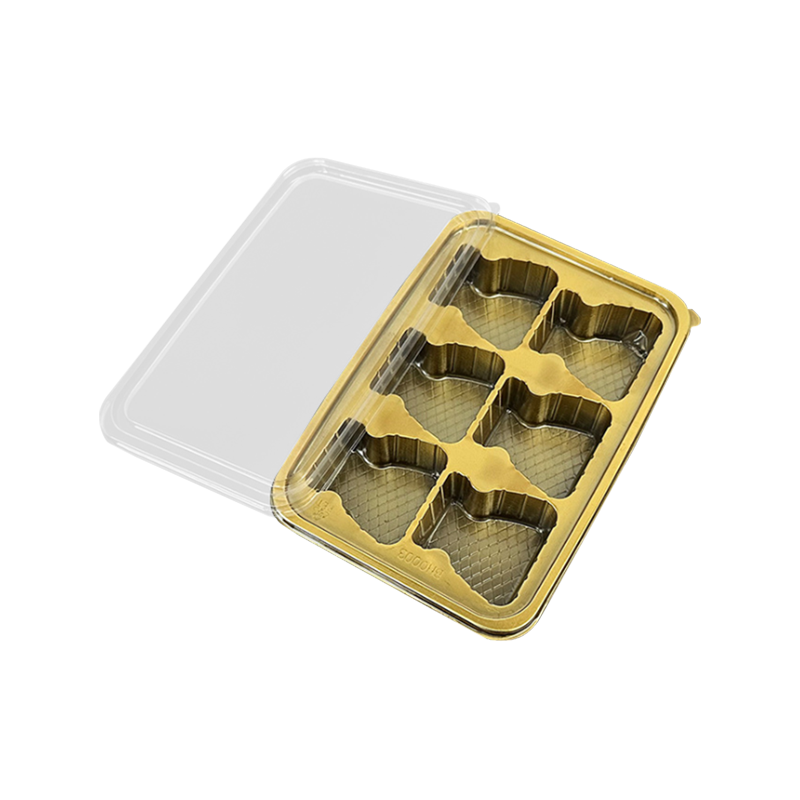
High Transparent or Color Choice: The transparent tray shows the delicate look of the dessert, while the colorful or gold base supports add a sense of premium.
Easy to separate and decorate: Many dessert trays are designed with multiple grids, which can avoid adhesions of different types of desserts and facilitate retail packaging.
Adapt to low temperature refrigeration: Refrigerated cakes, mousse and other desserts can be stored directly in a PP tray to maintain taste and freshness.
With the popularity of exquisite baking products, PP trays are used in the dessert industry and are widely used in the retail packaging of gift box combinations or pre-made desserts.
Airline and Group Meal Delivery
Airline meals, railway meals and large group meal companies have very high requirements for lunch boxes, and PP pallets are almost standard in this field.
Application Features:
Mass production: Airline meals and school group meals usually require hundreds to thousands of meals to be prepared at one time, and the batch forming capacity of PP trays can meet this high demand.
Strong heating adaptability: Air meals often need to be heated or kept warm during flight. The heat resistance of PP trays can ensure that no harmful substances are released during the heating process and will not be deformed due to high temperatures.
Reasonable design for partitions: the airline and group meal trays are mostly divided into 2-4 grids, and can hold main dishes, vegetables and meals at the same time, which is both convenient to eat and maintain the beautiful food.
Advantages:
Combined with high strength and lightweight: PP pallets are not only lightweight, reducing transportation burden, but also have sufficient toughness, suitable for repeated stacking and handling.
Customizable brand elements: Airlines, railway companies and large enterprises often print logos or LOGOs on the surface of the pallet to reflect the brand image and professionalism.
5. Environmental protection trends of PP plastic food trays
Use degradable or bio-based PP materials
Traditional PP plastics are derived from petroleum-based raw materials. The molecular structure is stable and not easy to decompose naturally. It often takes hundreds of years to degrade in the natural environment. This puts long-term pressure on the ecosystem. Research institutions and enterprises are developing biodegradable PP and bio-based PP (Bio-based PP) materials to reduce environmental burden.
The rise of bio-based PP materials
Bio-based PP refers to polypropylene synthesized through chemical or biotechnological routes based on renewable plant resources (such as corn, sugar cane, cassava, etc.). Compared with traditional petroleum-based PP, bio-based PP has the following advantages:
Reduce carbon footprint: Plant raw materials can absorb carbon dioxide during growth, partially offsetting the carbon emissions generated during production.
Strong renewable: The raw materials are widely sourced and do not rely on limited oil resources.
Compatible with traditional PP: The chemical structure of bio-based PP is similar to that of traditional PP, and existing production equipment can be used directly to avoid large-scale equipment transformation.
At present, some companies in Europe, Japan and the United States have achieved small-scale production of bio-based PP food pallets. Although its cost is slightly higher than that of ordinary PP, the price gap is expected to gradually narrow with the maturity of technology and the improvement of raw material supply chain.
Degradable and modified PP technology
In order to achieve partial degradation of PP materials in the natural environment, some companies have adopted the method of adding oxidizable degradants, photodegradants or biodegradable components to decompose PP into smaller molecular structures under specific conditions (such as ultraviolet irradiation and microbial action).
Oxidative degradation PP: By introducing breakable chemical bonds into the PP molecular chain, it accelerates its cleavage under high temperature or ultraviolet environment.
Biodegradation modification: Combine PLA (polylactic acid) or starch-based material with PP to improve the biodegradability of the material.
Biofilling and composite technology
In addition to directly using bio-based PP, companies have also tried to add natural fillers such as plant fibers, rice husk powder, bamboo fibers, etc. to the PP matrix, which not only reduces the use ratio of petroleum-based plastics, but also improves the environmental performance of the materials to a certain extent. This type of composite PP tray is lightweight, durable, and partially biodegradable, and is particularly suitable for the environmentally friendly packaging needs of high-end catering and takeaway brands.
Reduce overpackaging and design optimization
With consumers' pursuit of the concepts of "environmental protection" and "simplicity", reducing over-packaging has become another major trend in PP food pallets. In traditional takeaway lunch boxes and supermarket packaging, there is often the problem of "one lunch box + multi-layer bag + outer packaging box", which not only increases costs, but also causes a large amount of plastic waste.
Lightweight design
The structural design of PP pallets is developing towards the combination of lightweight and high strength. By optimizing the mold design, using reinforced rib structure or honeycomb bottom design, it is possible to reduce the amount of plastic while maintaining the strength and durability of the pallet. For example, some companies have successfully reduced material consumption by 20%-30% by thinning the wall thickness of the pallet or using hollow foaming technology, but do not affect the overall performance.
Integrated and multi-function packaging
In order to reduce matching plastic covers, linings and other accessories, some PP pallets adopt an integrated molding design, that is, the pallet comes with a foldable sealing structure, which is convenient for use and reduces the use of additional packaging components. At the same time, some designs allow trays to be used directly as tableware, realizing the function of "trays are dining trays" and reducing secondary waste.
Modularity and standardization
Takeaway and supermarket delivery require pallets of different specifications. If each pallet has a large difference in size, it will lead to waste of resources. The trend of standardized design is emerging: the bottom of the pallet, bayonet and other parts are produced according to unified specifications and can be matched with a variety of membrane sealing machines or automation equipment. This standardization not only reduces the waste of customized molds, but also facilitates classification and reuse of pallets after recycling.
Visual environmental design
In addition to functional optimization, some brands have printed environmentally friendly logos, recycling tips or added environmentally friendly slogans on pallets to guide consumers to actively participate in garbage sorting. This is not only a reflection of the company's fulfillment of environmental protection responsibilities, but also helps to improve the brand image.
Promote closed-loop recycling and reproduction systems
Recycling and reuse are one of the core means to achieve sustainable development of plastic packaging. PP materials have relatively high recyclability, but the current recovery rate is not ideal. In order to achieve a closed-loop cycle of "from pallet to pallet", a variety of measures are being taken in the industry.
Establish recycling networks and recycling classifications
Many countries and regions are strengthening garbage classification policies and clearly include PP containers in the category of recyclable plastics.
Enterprise independent recycling: Some large catering chain brands have begun to set up recycling points in their stores, encouraging customers to hand over used PP pallets for unified cleaning and recycling.
Third-party recycling platform: Cooperate with recycling companies to process waste PP pallets into recycled PP particles through recycled plastic factories, and then invest in new pallet production.
Development of food-grade recycled PP (rPP)
Traditional recycled PP is often used in non-food contact products, such as flower pots, garbage cans, etc. However, with the breakthrough of food-grade regeneration technology, enterprises can produce food-grade rPP that meets FDA and EFSA standards through high-temperature degassing, removing odors, filtering impurities and other processes to produce new food trays. This closed-loop utilization not only reduces the use of native plastics, but also reduces carbon emissions.
Intelligent traceability and recycling incentive mechanism
Some innovative companies add QR codes or RFID tags to the pallet to achieve product traceability. Consumers can obtain recycling information or environmental protection points after scanning, increasing recycling motivation. This model is gradually promoted in fast food chains and takeaway industries in Europe, Japan and South Korea.
Green supply chain and carbon emission control
In addition to innovation in materials and recycling, environmental protection trends are also reflected in the green management of the entire supply chain.
Energy-saving production: Manufacturers reduce production energy consumption by optimizing injection molding equipment and introducing energy-saving motors and automation systems.
Logistics emission reduction: Lightweight PP pallets can reduce transportation energy consumption, especially in large-scale catering and supermarket distribution links, which helps reduce carbon emissions.
Environmental certification: More and more companies are applying for ISO14001 environmental management system or carbon footprint certification to meet the requirements of the international market for green supply chains.
Future development trends and challenges
Promotion of regulations and industry standardization
Environmental protection regulations in the EU, the United States, China and other places are becoming increasingly strict, and restrictions on disposable plastic packaging are putting forward, forcing companies to accelerate the development of environmentally friendly PP pallets. In the future, unified food-grade rPP standards and environmentally friendly labeling specifications will help the healthy development of the industry.
Cost and consumer acceptance
Although environmentally friendly PP pallets have advantages, bio-based materials and recycling technologies are currently costly and have limited market popularity. Enterprises need to balance price, environmental protection and functionality, and improve consumers' sense of environmental protection through education and publicity.
Technological breakthroughs and innovations
In the future, with the development of chemical recycling and carbon capture technology, the production and recycling of PP pallets will be more efficient and environmentally friendly. At the same time, biodegradable PP and edible coatings may also become new directions for the next generation of environmentally friendly packaging.
- The company requires rigorous, using a high starting point, trustworthy, quality, and actively develop and innovate, the pursuit of excellence route!
CONTACT US
- Tel: +86-18867945666
- E-mail: [email protected]
- Add: No.11 Huafeng Road, Anhua Community, Anhua Town, Zhuji City, Shaoxing, Zhejiang, China
GET A QUOTE
Copyright @ Donghang Polymer Material Technology Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved.




 English
English عربى
عربى Español
Español